Ten things to know about subsidized rental housing in Alberta
Ten things to know about subsidized rental housing in Alberta
- Housing need has been increasing in Alberta. The percentage of Alberta households in core housing need has been rising steadily over the past three Census periods. In 2006, 10.1% of Alberta households were in core housing need; by 2011, this figure had risen to 10.7%; and in 2016, the figure stood at 11.4%. In 2016, this represented more than 164,000 Alberta households.
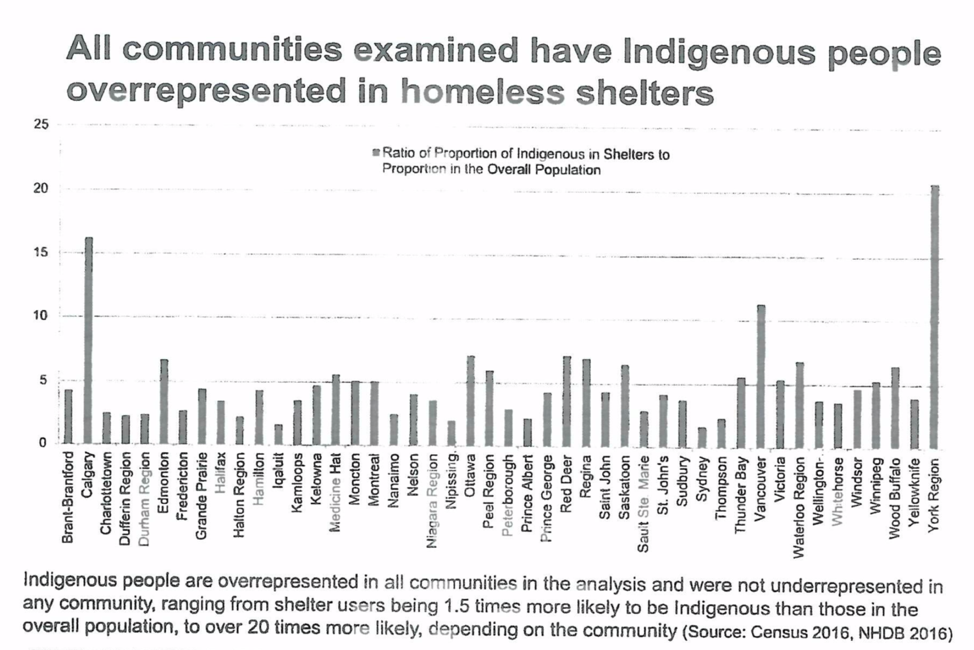
- Some household types face especially dire circumstances. Across Alberta, 30.6% of female lone-parent families are in core housing need, while 30.8% of seniors living alone are in core housing need. Further, the rate of core housing need for Status Indians is more than double the rate for non-Indigenous households (and these figures do not account for households living on reserve).[1]
- More than one in four persons experiencing absolute homelessness in Alberta is Indigenous. That’s according to Alberta’s 2018 Point-in-Time Count. It’s worth noting that Indigenous peoples make up just 7% of Alberta’s total population.
- On a per capita basis, Alberta has far fewer subsidized housing units than the rest of Canada.[2] According to the most recent Census, subsidized housing represents just 2.9% of Alberta’s housing units; for Canada as a whole, the figure is 4.2%.
- Comparing Alberta to British Columbia is instructive. As can be seen below, from 2007 until 2010, Alberta produced more housing units funded unilaterally by the provincial government than BC on an annual basis. But since 2011, BC has been outperforming Alberta in that respect. In fact, in 2017, BC’s provincial government funded more than 15 times as many housing units than Alberta, despite having a roughly similar overall population, and despite Alberta having an NDP government at the time.[3]
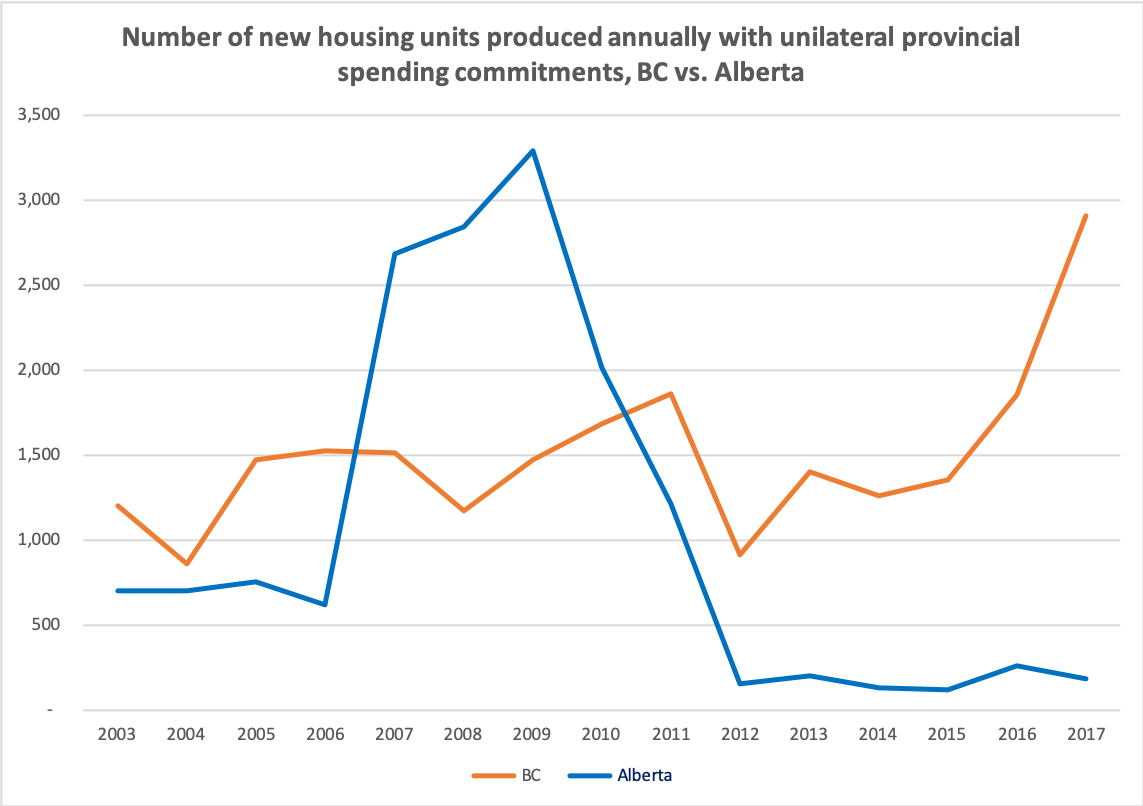
Note. Figures compiled by David Macdonald and Greg Suttor using provincial reporting. Figures only include unilateral provincial spending, and do not include cost-shared initiatives.
- The impact of Canada’s National Housing Strategy will be modest. Recent analysis by Canada’s Parliamentary Budget Officer projects future federal housing spending to actually decrease over the next decade (relative to GDP). The same analysis projects that total spending on Indigenous housing by Canada’s federal government will be “substantially lower” going forward.
- When Alberta’s provincial government does fund new subsidized units, the process lacks transparency. Even when Rachel Notley’s NDP government was in power, housing funding was not allocated via a formal grant program through which non-profits (i.e., community housing/non-market housing providers) could apply for funding. Such a process has not been in place in Alberta since 2012.
- The Government of Alberta lacks a clear, public reporting structure for provincially-subsidized housing. For example, most Albertans—including very well- placed sources in the affordable housing sector—do not know: how much recent funding was used for repairs vs. new builds; how much of this funding has been dependent on cost-matching from other orders of government; what types of projects have received the funding; which types of households have been targeted; or to which municipalities the funding has flowed. This lack of transparency makes it very challenging for key actors in the non-profit housing and homeless-serving sectors to plan; it has also made it virtually impossible for key players in the sector to have a democratic dialogue about how public dollars are being allocated.
- In October 2019, the UCP government unveiled its first budget, announcing some housing cuts. Starting in 2020, operating budgets for Housing Management Bodies (HMBs) will be reduced by an average of 3.5%. There will also be a 24% reduction to the Rental Assistance Program, which provides financial assistance for low- to moderate-income households to assist with monthly rent payments for up to one year. This 24% reduction begins in 2020 and takes full effect within three years.
- There has been long-time speculation that the recent provincial funding reduction (or a portion of it) may be retargeted and used to match federal funding through the new Canada Housing Benefit. That program, set to take effect 1 April 2020, requires that the Government of Alberta match federal funding.[4] This speculation was confirmed in a 26 December 2019 Canadian Press article.
In sum. There is need for both more subsidized rental housing in Alberta and more transparency at the provincial level. In its upcoming provincial budget, the Jason Kenney government has the opportunity to address both issues.
Acknowledgements. I wish to thank the following individuals for invaluable assistance with this blog post: Zain Abedin, Damian Collins, Martina Jileckova, Jonn Kmech, Ron Kneebone, David Macdonald, Jedd Matechuk, Katrina Milaney, Jeff Morrison, Jenny Morrow, Steve Pomeroy, John Rook, Greg Suttor, Vincent St-Martin and one anonymous source. Any errors are mine.
[1] Rates of core housing need are not calculated in many of Canada’s First Nations communities, largely because in order to calculate core housing need, one must know the cost of market housing (which often does not exist in First Nations’ communities).
[2] According to Statistics Canada’s 2016 Census of Population, subsidized housing “includes rent geared to income, social housing, public housing, government-assisted housing, non-profit housing, rent supplements and housing allowances.”
[3] According to the 2016 Census, Alberta had a total population of 4,067,175, while BC had a total population of 4,648,055.
[4] The Canada Housing Benefit is expected to provide an average of $2,500/annually, per eligible household, to Canadians in housing need.